A few months ago, we shared detailed information about the changes we expected to make in WebXPRT 4. We are currently doing internal testing of the WebXPRT 4 Preview build in preparation for releasing it to the public. We want to let our readers know what to expect.
We’ve made some changes since our last update and some of the details we present below could still change before the preview release. However, we are much closer to the final product. Once we release the WebXPRT 4 Preview, testers will be able to publish scores from Preview build testing. We will limit any changes that we make between the Preview and the final release to the UI or features that are not expected to affect test scores.
General changes
Some of the non-workload changes we’ve made in WebXPRT 4 relate to our typical benchmark update process.
- We have updated the aesthetics of the WebXPRT UI to make WebXPRT 4 visually distinct from older versions. We did not significantly change the flow of the UI.
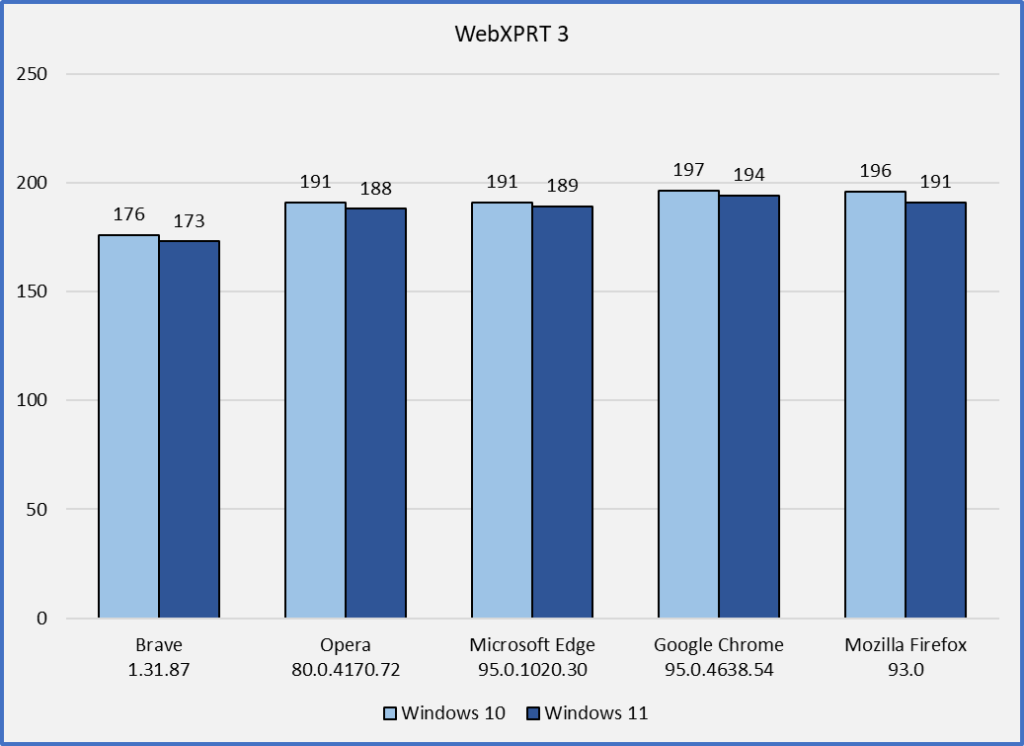
- We have updated content in some of the workloads to reflect changes in everyday technology, such as upgrading most of the photos in the photo processing workloads to higher resolutions.
- We have not yet added a looping function to the automation scripts, but are still considering it for the future.
- We investigated the possibility of shortening the benchmark by reducing the default number of iterations from seven to five, but have decided to stick with seven iterations to ensure that score variability remains acceptable across all platforms.
Workload changes
- Photo Enhancement. We increased the efficiency of the workload’s Canvas object creation function, and replaced the existing photos with new, higher-resolution photos.
- Organize Album Using AI. We replaced ConvNetJS with WebAssembly (WASM) based OpenCV.js for both the face detection and image classification tasks. We changed the images for the image classification tasks to images from the ImageNet dataset.
- Stock Option Pricing. We updated the dygraph.js library.
- Sales Graphs. We made no changes to this workload.
- Encrypt Notes and OCR Scan. We replaced ASM.js with WASM for the Notes task and updated the WASM-based Tesseract version for the OCR task.
- Online Homework. In addition to the existing scenario which uses four Web Workers, we have added a scenario with two Web Workers. The workload now covers a wider range of Web Worker performance, and we calculate the score by using the combined run time of both scenarios. We also updated the typo.js library.
Experimental workloads
As part of the WebXPRT 4 development process, we researched the possibility of including two new workloads: a natural language processing (NLP) workload, and an Angular-based message scrolling workload. After much testing and discussion, we have decided to not include these two workloads in WebXPRT 4. They will be good candidates for us to add as experimental WebXPRT 4 workloads in 2022.
The release timeline
Our goal is to publish the WebXPRT 4 preview build by December 15th, which will allow testers to publish scores in the weeks leading up to the Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas in January 2022. We will provide more detailed information about the GA timeline here in the blog as soon as possible.
If you have any questions about the details we’ve shared above, please feel free to ask!
Justin