A few months ago, we discussed some initial ideas for the next version of HDXPRT, including updating the benchmark’s workloads and real-world trial applications and improving the look and feel of the UI. This week, we’d like to share more about the status of the HDXPRT development process.
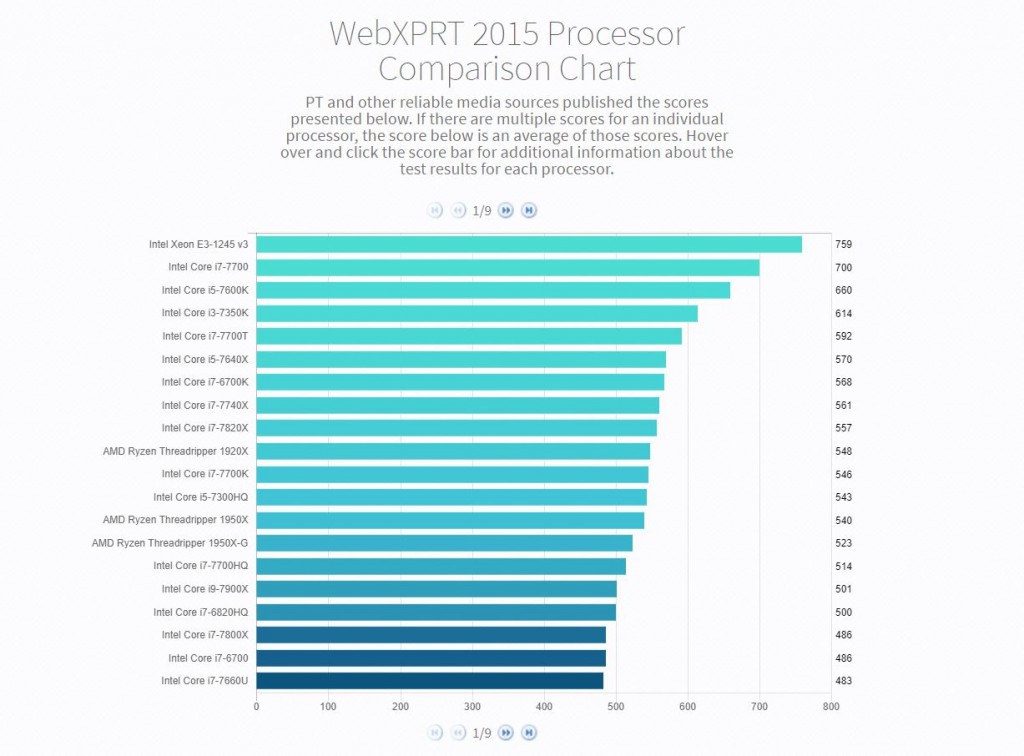
We’re planning to keep HDXPRT’s three test categories: editing photos, editing music, and converting videos. We’re also planning to use the latest trial versions of the same five applications included in HDXPRT 2014: Adobe Photoshop Elements, Apple iTunes, Audacity, CyberLink MediaEspresso, and HandBrake. The new versions of each of these programs include features and capabilities that may enhance the HDXPRT workloads. For example, Adobe Photoshop Elements 2018 includes interesting new AI tools such as “Open Closed Eyes,” which purports to fix photos ruined by subjects who blinked at the wrong time. We’re evaluating whether any of the new technologies on offer will be a good fit for HDXPRT.
We’re also evaluating how the new Windows 10 SDK and Fall Creators Update will affect HDXPRT. It’s too early to discuss potential changes in any detail, but we know we’ll need to adapt to new development tools, and it’s possible that the Fluent Design System will affect the HDXPRT UI beyond the improvements we already had in mind.
As HDXPRT development progresses, we’ll continue to keep the community up to date. If you have suggestions or insights into the new Fall Creators Update or any of HDXPRT’s real-world applications, we’d love to hear from you! If you’re just reading out about HDXPRT for the first time, you can find out more about the purpose, structure, and capabilities of the test here.
Justin